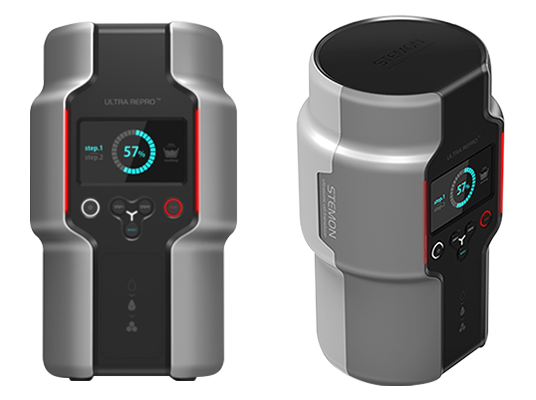
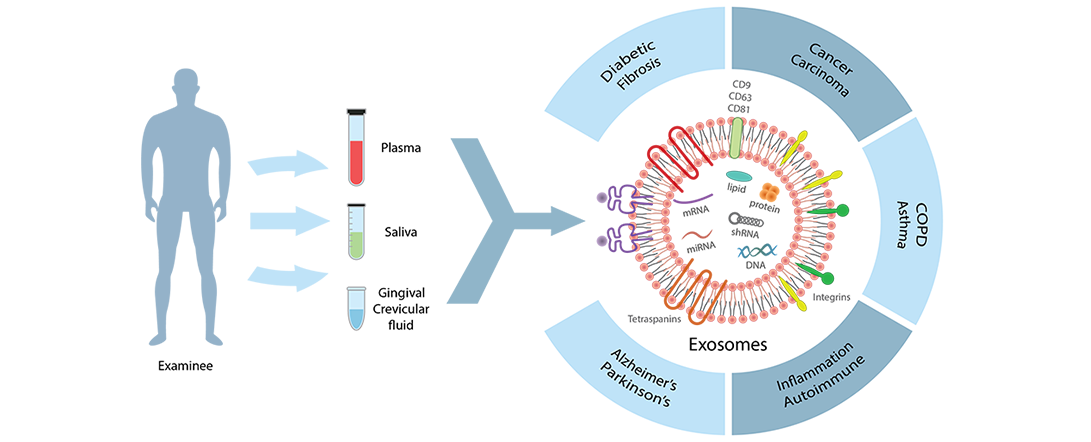
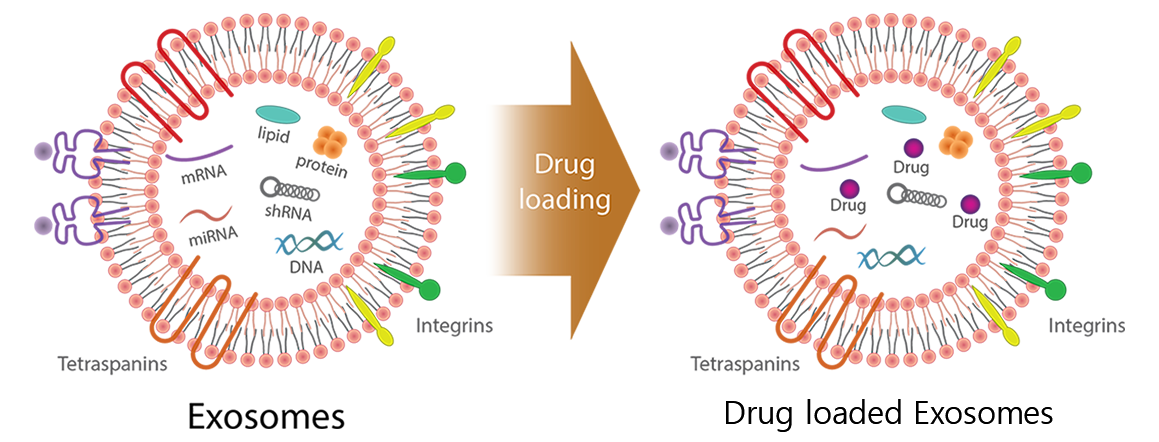
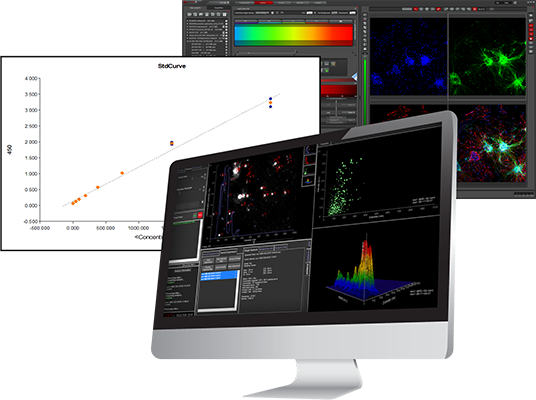
Exosome
- Cells secrete exosomes to exchange information with each other.
- The exosomes in intracellular MVB (Multi-vesicular body) are secreted by fusion of MVB and cell membranes and transferred to the recipient cell.
- Exosomes have a phospholipid bilayer structure with a size of about 30-150 nm.
- Exosomes contain various nucleic acids, lipids and proteins such as growth factors and cytokines, etc.
Recent Trends of Exosome Research

Exosome research trends in the last 20 years
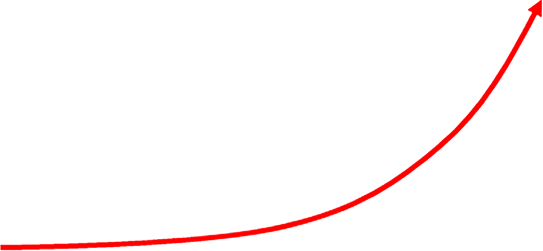
Year
Source: PubMed, (2001-2021)
- Recent studies on exosomes are very active because exosomes show various biological activities reflecting the characteristics of the cells secreting them.
- Recently, academic papers related to exosomes have increased by an average of 30.4% over the past 10 years.
Key Research on Exosomes

-
1983
Confirmation of exosome existence.
-
1996
Functional study of exosome, role of Immunoregulatory, etc.
-
1998 ~ 2001
Study of DC and cancer cell-derived from exosome, etc.
-
2006 ~ 2007
Confirmed cell signal transduction and presence of RNA and miRNA
-
2013
Analysis of exosome properties, etc. (CD9, CD63, CD81)
-
2010 ~ 2020
Increased studies in diagnosis and drug delivery system research
The Necessity and Limitations of Various Exosomes.

The characteristics of exosomes vary depending on tissues and cells, which makes a necessity of suitable exosome for research purposes
-

Difficulty of securing exosome
-

Burden of time and expenses
-

Special equipment for
exosome analysis is required